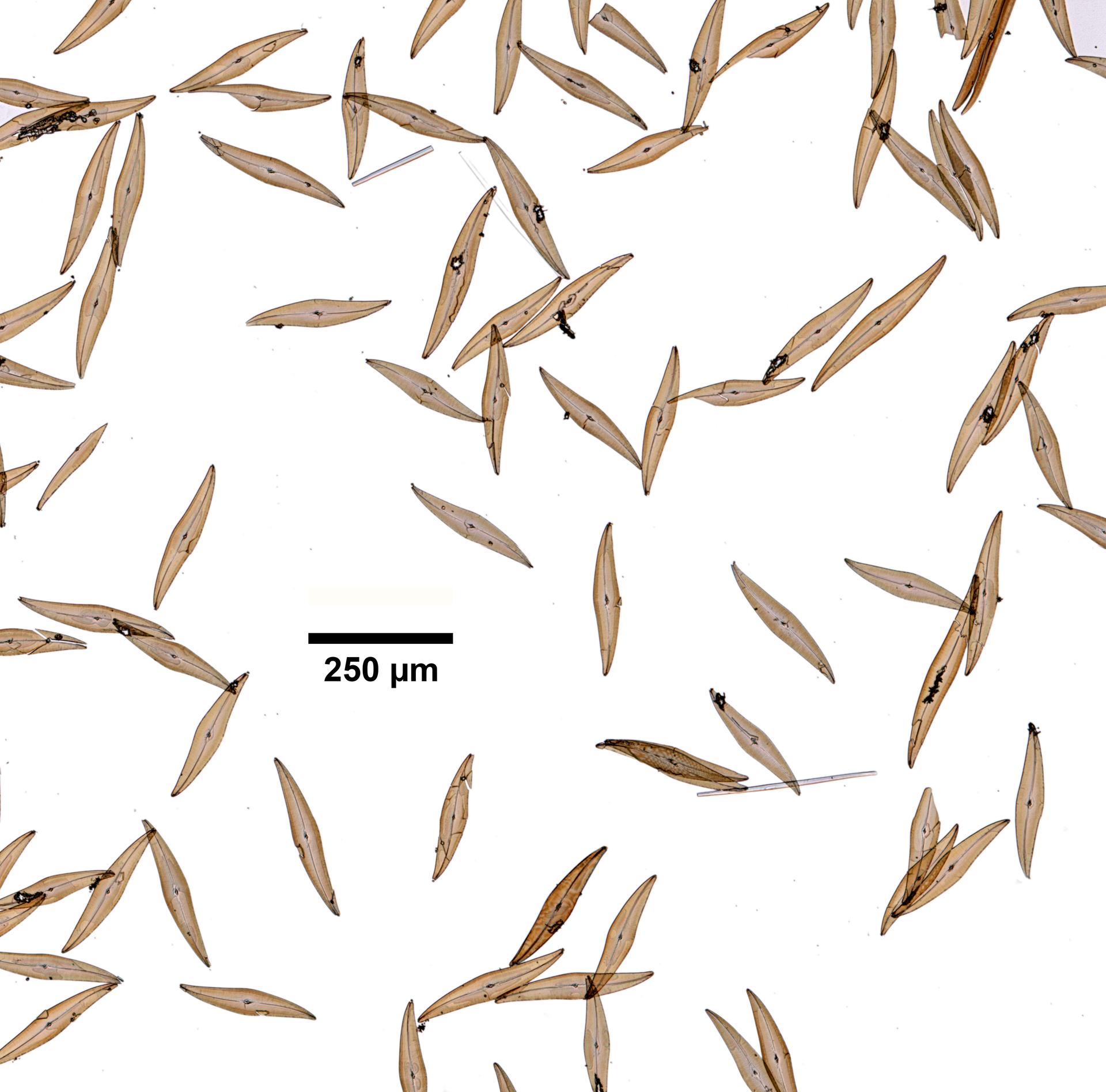
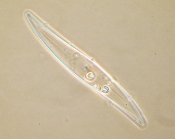
Scheldt species name details
Pleurosigma angulatum (Queckett) W.Smith, 1852
149183 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:149183)
uncertain > unassessed
Species
brackish
Smith, W. (1852). Notes on the Diatomaceae with descriptions of British Species included in the genus Pleurosigma. Annals and Magazine of Natural History, 2nd series,, 9: 1-12, 2 pls.
page(s): p. 7; pl. 1, fig. 7, pl. 1, fig. 9 [details]
Sterrenburg, F.A.S. (1991). Studies on the genera Gyrosigma and Pleurosigma (Bacillariophyceae). The typus generis of Pleurosigma, some presumed varieties and imitative species. Botanica Marina, 34(6): 561-573
page(s): v. 35(6): p. 566; fig. 2-34 [details]
(of ) Quekett, J.T. (1848). A Practical treatise on the use of the microscope including the different methods of preparing and examining animal, vegetable, and mineral structures. London, pp. 1-xxi, 1-464, fig. 1-241 + 9 pls.
page(s): p. 438; pl. 8, fig. 4-7 [details]
page(s): p. 7; pl. 1, fig. 7, pl. 1, fig. 9 [details]
Sterrenburg, F.A.S. (1991). Studies on the genera Gyrosigma and Pleurosigma (Bacillariophyceae). The typus generis of Pleurosigma, some presumed varieties and imitative species. Botanica Marina, 34(6): 561-573
page(s): v. 35(6): p. 566; fig. 2-34 [details]
(of ) Quekett, J.T. (1848). A Practical treatise on the use of the microscope including the different methods of preparing and examining animal, vegetable, and mineral structures. London, pp. 1-xxi, 1-464, fig. 1-241 + 9 pls.
page(s): p. 438; pl. 8, fig. 4-7 [details]
Kociolek, J.P.; Blanco, S.; Coste, M.; Ector, L.; Liu, Y.; Karthick, B.; Kulikovskiy, M.; Lundholm, N.; Ludwig, T.; Potapova, M.; Rimet, F.; Sabbe, K.; Sala, S.; Sar, E.; Taylor, J.; Van de Vijver, B.; Wetzel, C.E.; Williams, D.M.; Witkowski, A.; Witkowski, J. (2021). DiatomBase. Pleurosigma angulatum (Queckett) W.Smith, 1852. Accessed through: VLIZ Consortium Scheldt Species Register at: https://scheldemonitor.org/speciesregister/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=149183 on 2025-09-12
VLIZ Consortium. Scheldt Species Register. Pleurosigma angulatum (Queckett) W.Smith, 1852. Accessed at: https://scheldemonitor.be/speciesregister/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=149183 on 2025-09-12
Date
action
by
2005-03-30 08:52:46Z
created
db_admin
2018-01-31 09:33:29Z
changed
db_admin
original description
Smith, W. (1852). Notes on the Diatomaceae with descriptions of British Species included in the genus Pleurosigma. Annals and Magazine of Natural History, 2nd series,, 9: 1-12, 2 pls.
page(s): p. 7; pl. 1, fig. 7, pl. 1, fig. 9 [details]
original description Sterrenburg, F.A.S. (1991). Studies on the genera Gyrosigma and Pleurosigma (Bacillariophyceae). The typus generis of Pleurosigma, some presumed varieties and imitative species. Botanica Marina, 34(6): 561-573
page(s): v. 35(6): p. 566; fig. 2-34 [details]
original description (of ) Quekett, J.T. (1848). A Practical treatise on the use of the microscope including the different methods of preparing and examining animal, vegetable, and mineral structures. London, pp. 1-xxi, 1-464, fig. 1-241 + 9 pls.
page(s): p. 438; pl. 8, fig. 4-7 [details]
context source (Schelde) Maris, T., O. Beauchard, S. Van Damme, E. Van den Bergh, S. Wijnhoven & P. Meire. (2013). Referentiematrices en Ecotoopoppervlaktes Annex bij de Evaluatiemethodiek Schelde-estuarium Studie naar “Ecotoopoppervlaktes en intactness index”. [Reference matrices and Ecotope areas Annex to the Evaluation methodology Scheldt estuary Study on “Ecotope areas and intactness index”. <em>Monitor Taskforce Publication Series, 2013-01. NIOZ: Yerseke.</em> 35 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
basis of record Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details]
additional source Tomas, C.R. (Ed.). (1997). Identifying marine phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780126930184 [details]
additional source Linkletter, L. E. (1977). A checklist of marine fauna and flora of the Bay of Fundy. <em>Huntsman Marine Laboratory, St. Andrews, N.B.</em> 68: p. [details]
additional source Martin, J. L.; LeGresley, M. M. ; Strain, P. M. (2001). Phytoplankton monitoring in the Western Isles region of the Bay of Fundy during 1997-98. <em>Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2349.</em> 4: 1-85. [details]
additional source Thomas, M. L. H. (1983). Marine and coastal systems of the Quoddy Region, New Brunswick. <em>Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences.</em> 64:1-306. [details] Available for editors
additional source Hällfors, G. (2004). Checklist of Baltic Sea Phytoplankton Species (including some heterotrophic protistan groups). <em>Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings.</em> No. 95: 210 pp., available online at http://helcom.fi/Lists/Publications/BSEP95.pdf [details] Available for editors
additional source Fourtanier, E. & Kociolek, J. P. (compilers). (2011). Catalogue of Diatom Names. California Academy of Sciences, On-line Version. Updated 2011-09-19., available online at http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/diatoms/names/index.asp [details]
additional source Krayesky, D. M.; Meave, D. C.; Zamudio, E.; Norris, E.; Fredericq, S.; Tunnell, J. (2009). Diatoms (Bacillariophyta) of the Gulf of Mexico. <em>Gulf of Mexico origin, waters, and biota.</em> 1: 155-186. [details] Available for editors
additional source Lakkis, S. (2011). Le phytoplancton marin du Liban (Méditerranée orientale): biologie, biodiversité, biogéographie. Aracne: Roma. ISBN 978-88-548-4243-4. 293 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Meunier, A. (1915). Microplankton de la Mer Flamande: 2. Les Diatomacées (suite) (Le Genre Chaetoceros excepté). Mémoires du Musée Royal d'Histoire Naturelle de Belgique = Verhandelingen van het Koninklijk Natuurhistorisch Museum van België, VII(3). Hayez, imprimeur de l'Académie royale de Belgique: Bruxelles. 182 pp. [details]
page(s): p. 7; pl. 1, fig. 7, pl. 1, fig. 9 [details]
original description Sterrenburg, F.A.S. (1991). Studies on the genera Gyrosigma and Pleurosigma (Bacillariophyceae). The typus generis of Pleurosigma, some presumed varieties and imitative species. Botanica Marina, 34(6): 561-573
page(s): v. 35(6): p. 566; fig. 2-34 [details]
original description (of ) Quekett, J.T. (1848). A Practical treatise on the use of the microscope including the different methods of preparing and examining animal, vegetable, and mineral structures. London, pp. 1-xxi, 1-464, fig. 1-241 + 9 pls.
page(s): p. 438; pl. 8, fig. 4-7 [details]
context source (Schelde) Maris, T., O. Beauchard, S. Van Damme, E. Van den Bergh, S. Wijnhoven & P. Meire. (2013). Referentiematrices en Ecotoopoppervlaktes Annex bij de Evaluatiemethodiek Schelde-estuarium Studie naar “Ecotoopoppervlaktes en intactness index”. [Reference matrices and Ecotope areas Annex to the Evaluation methodology Scheldt estuary Study on “Ecotope areas and intactness index”. <em>Monitor Taskforce Publication Series, 2013-01. NIOZ: Yerseke.</em> 35 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
basis of record Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details]
additional source Tomas, C.R. (Ed.). (1997). Identifying marine phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780126930184 [details]
additional source Linkletter, L. E. (1977). A checklist of marine fauna and flora of the Bay of Fundy. <em>Huntsman Marine Laboratory, St. Andrews, N.B.</em> 68: p. [details]
additional source Martin, J. L.; LeGresley, M. M. ; Strain, P. M. (2001). Phytoplankton monitoring in the Western Isles region of the Bay of Fundy during 1997-98. <em>Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2349.</em> 4: 1-85. [details]
additional source Thomas, M. L. H. (1983). Marine and coastal systems of the Quoddy Region, New Brunswick. <em>Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences.</em> 64:1-306. [details] Available for editors
additional source Hällfors, G. (2004). Checklist of Baltic Sea Phytoplankton Species (including some heterotrophic protistan groups). <em>Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings.</em> No. 95: 210 pp., available online at http://helcom.fi/Lists/Publications/BSEP95.pdf [details] Available for editors
additional source Fourtanier, E. & Kociolek, J. P. (compilers). (2011). Catalogue of Diatom Names. California Academy of Sciences, On-line Version. Updated 2011-09-19., available online at http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/diatoms/names/index.asp [details]
additional source Krayesky, D. M.; Meave, D. C.; Zamudio, E.; Norris, E.; Fredericq, S.; Tunnell, J. (2009). Diatoms (Bacillariophyta) of the Gulf of Mexico. <em>Gulf of Mexico origin, waters, and biota.</em> 1: 155-186. [details] Available for editors
additional source Lakkis, S. (2011). Le phytoplancton marin du Liban (Méditerranée orientale): biologie, biodiversité, biogéographie. Aracne: Roma. ISBN 978-88-548-4243-4. 293 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Meunier, A. (1915). Microplankton de la Mer Flamande: 2. Les Diatomacées (suite) (Le Genre Chaetoceros excepté). Mémoires du Musée Royal d'Histoire Naturelle de Belgique = Verhandelingen van het Koninklijk Natuurhistorisch Museum van België, VII(3). Hayez, imprimeur de l'Académie royale de Belgique: Bruxelles. 182 pp. [details]
 Present
Present  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (301 publications)
To Catalogue of Diatom Names (CAS)
To Catalogue of Diatom Names (CAS)
To Dyntaxa
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Pleurosigma angulatum)
To GenBank (2 nucleotides; 1 proteins)
To PESI
To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 093856)
To ITIS
To Catalogue of Diatom Names (CAS)
To Catalogue of Diatom Names (CAS)
To Dyntaxa
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Pleurosigma angulatum)
To GenBank (2 nucleotides; 1 proteins)
To PESI
To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 093856)
To ITIS